- Four are the same for both streams (compulsory modules - 15 credits each)
- The other four (15 credits each) are different for the two streams.
In May the final examinations for the taught modules will take place and in their third term (June - September) students will complete the final dissertation.
You have the option to choose one of two specialisations, or ‘streams, ’ for your dissertation:
- Thermofluids, or
- Solid Body Mechanics.
The structure of the course is summarised in the scheme below:
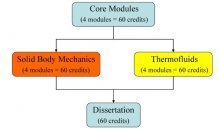
Compulsory Modules
Strategic Management, Innovation and EnterprisePrepares graduate engineers to perform the managerial and business functions expected of staff in first level management positions in engineering organisations. Main topics include: financial ownership issues; human resources management; organisation of a business; marketing concept; ethical business; marketing communications.
Research Methods and Sustainable Engineering
Instil principles of good research practice and enable students to acquire skills to conduct scientifically-robust research with due consideration of engineering quality issues and environmental and health and safety risks. Students will develop a multi-disciplinary understanding of sustainable development and develop a portfolio of environmental impact appraisal tools to apply as future practicing engineers.
Main topics include: practical research issues; information retrieval; risk management; scientific communication, research dissemination; sustainable engineering, including but not limited to sustainable development concepts and policy drivers, Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), environmental impact appraisal tools, with the help of case studies.
Advanced Modelling and DesignProvides students with the ability to employ advanced numerical models for the analysis of complex engineering problems. Main topics include: finite element analysis: two-dimensional elements: triangular, quadrilateral and isoparametric; applications to steady and transient heat transfer; applications to two-dimensional stress analysis; optimisation: types of optimisation problems; objective function; constrained and unconstrained optimisation; multivariate search methods, penalty function, Lagrange multipliers; applications to linkage synthesis; manufacture: computer applications in manufacturing practice, optimisation in design for manufacture, management procedures and quality requirements, application to company practice; design: use and application of Computer Aided Engineering Software in engineering manufacture; the integration of computer aided engineering and manufacturing methods in company practice.
Computer Aided Engineering 1
Shows how the entities points, edges, surfaces and solids are modelled for CAE and how to use their implementation on contemporary CAE software to create the computer model of a part or assembly. Covers some useful applications of computer models such as mechanism synthesis and analysis, NC manufacture and Rapid Prototyping. Provides the skill on the use of a contemporary CAE package for Mechanism Analysis, NC code generation and Rapid Prototyping. Main topics include:
- Representation and manipulation of the entities points, lines and curves, surfaces and solids (components and assemblies) for use in CAD/CAM applications, with a hands on training in a contemporary CAE system.
- Analysing the motion aspects (position, velocity and acceleration) and force aspects of connected links or chains used in products (Dynamics).
- The use of a CAE package for analysing mechanisms.
- Basics of NC manufacturing and the use of a contemporary CAE package for generating NC codes.
- Principles of Rapid Prototyping (RP) and the use of a RP system and a contemporary CAD software
Dissertation (Individual project)
Optional Modules
Choose one of the two themes below:
Theme 1 – Thermofluids
- Advanced Thermofluids: Includes advanced experimental and modelling research tools in thermofluids. Main topics include: methods and instruments in fluid flow measurements: laser doppler anemometry (LDA), particle image velocimetry (PIV), hot-wire anemometry (HWA); Fluid flow and heat transfer simulations by Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) modelling, large eddy simulation (LES) and direct numerical simulation (DNS).







